|
|
|
CRITICAL VEHICLE SYSTEMS AND SUBSYSTEMS
A. CONSTRUCTION OF THE AUTOMOBILE Frame and Body The purpose of a vehicle's frame is to support the body, engine, and other components. The frame along with the body is largely responsible for the structural integrity of the vehicle. The frame itself is supported by the wheels and tires through the vehicle's suspension system. EngineWhen you start your car: (a) power from your battery is used to operate a small electric motor called the starter motor, (b) the starter motor turns the flywheel and crank shaft of the engine so that the engine can attain sufficient momentum and speed to start and run on its own, (c) the crankshaft is inside your engine and supplies power to the remainder of the power train, (d) the crankshaft is also connected by connecting rods to pistons inside cylinders, (e) exploding gas inside the cylinders drives the pistons up and down and, through the connecting rods, turns the crankshaft, (f) inside the cylinders a mixture of gas and air is compressed, ignited by a spark plug , and explodes, and (g) the mixture of air and gas is delivered to the cylinders by a carburetor and intake manifold or a fuel injection system. The moving parts of your engine must be lubricated. Oil which accumulates in your engine's oil pan is pumped by the oil pump through an oil filter and then through tubes that deliver the oil to the moving parts that need to be lubricated.
Vehicle systems, steering A vehicle's steering wheel is attached to a steering column or shaft which terminates in the steering box. Inside the steering box, the turning motion of the column is translated into a lateral motion which is passed on to the wheels through a series of components which include ball joints , the steering arm , and the steering knuckle. In power steering systems, turning of the steering wheel actuates a hydraulic system which amplifies the forces necessary to rotate and move the linkages leading to the wheels. When you turn the steering wheel in a power steering system you cause hydraulic fluid to be compressed inside a hydraulic cylinder and transmitted by hydraulic lines to a piston which amplifies the force making it easier to turn the wheels. In order for the hydraulic system to operate, the engine must be running. Vehicle systems, suspension The purpose of your vehicle's suspension system is to (a) connect the wheels to the frame and body and (b) keep the movement of your wheels from being transmitted fully to the body. This allows you to maintain control of the car in turns, when you hit pot holes, and on rough roads. It also makes riding in the car more comfortable. The up and down movement of your wheels is absorbed by the springs in your suspension system, your shock absorbers keep the springs from continuing to bounce, and there are different designs for suspension systems involving various linkages, struts, joints, torsion bars, and so on. Vehicle systems, electrical The (a) battery is your vehicle's primary source of electrical power, (b) when you turn your ignition switch to start your car electricity is used to close another switch called a solenoid that transmits the large amount of current needed to turn the starter motor, (c) once your engine is running, power is generated by the alternator which also keeps your battery charged, (d) your voltage regulator controls the amount of electricity that is generated, (e) your distributor and coil generate and deliver the very high voltage electricity needed by the individual spark plugs of your engine, (f) electricity is distributed throughout your vehicle by various electrical circuits for lighting, to operate electrical motors, to operate computers that control various functions, to operate your radio, interior cooling, heating, and ventilating system, and so on, and (g) the purpose of fuses is to disable a circuit that is drawing too much current so as to prevent a fire and protect the components that the circuit serves. Vehicle systems, fuel Fuel and air is delivered to the engine through components which include:
Vehicle systems, power train A vehicle's power train consists of components that generate and transmit power to the wheels. In a rear-wheel drive vehicle, the power train includes:
In a front-wheel drive vehicle, the power is transmitted from the engine through a combination transmission-differential and then directly to the front wheels. In a four-wheel drive vehicle, the power is transmitted from the transmission to a transfer case which can transmit power to either the rear wheels only or to both the rear and front wheels. Vehicle systems, exhaust After gas is exploded in the cylinders of the engine:
Vehicle systems, cooling The heat caused by the friction of moving engine parts and the explosion of gasoline in the cylinders is removed through the vehicle's cooling system. The
basic components of your car's cooling system include a radiator, fan, water
pump, thermostat, an overflow tank, water, coolant, and a series of belts,
clamps and hoses to connect it all together and make it run. The system works by
directing fluid past the hottest parts of your engine (the cylinder heads and
valves), then redirecting that fluid out to the radiator, where the heat
collected from the cylinder heads gets dissipated into the cooler atmosphere.
Then the whole process begins again. Cooling system components:
Vehicle systems, braking There are two independent braking systems in your vehicle, the service brakes and the parking brake (also referred to as the emergency brake ). The service brakes are used to slow your vehicle while you are driving. The parking brake can also be used to slow your vehicle in an emergency, but is mainly used to hold your vehicle in one place while stopped or parked. When you press your brake pedal, a piston in your master cylinder forces brake fluid through hydraulic lines to pistons in the wheel cylinders at the wheels where additional pistons provide the force to apply your brakes. Hydraulic fluid is stored in a brake fluid reservoir normally located in the engine compartment. There are two types of brakes:
Drum brakes slow your vehicle by the friction of a brake shoe pushing against the drum which is rotating with the wheel. Disc brakes slow your car by the friction of a caliper pressing against a disc which is rotating with the wheel. Both drum and disk brakes convert friction force to heat and if the brakes get too hot, they cease to work because they cannot dissipate enough heat. For both types of brakes, your stopping distance time is roughly proportional to the square of your speed, so if you double your speed you quadruple the distance to stop your car. When you are stopped and apply your brakes, they lock. It is the friction force between the tires and the road that keeps you from moving. Your parking brake uses a cable rather than a hydraulic system to engage your brakes or clamp down on your drive shaft and will therefore function even if your service brakes have failed. Brakes will only slow your car while there is friction between the moving parts of your brakes. If the wheels are locked as is the case of a skid, the drums or discs are not moving and there will be no friction. The purpose of antilock brake systems is to prevent the brakes from becoming locked by first sensing if they are locked and then automatically, rapidly releasing and applying pressure. If you do not have antilock brakes, you can avoid having your brakes lock by manually, rapidly releasing and then reapplying pressure to your brake pedal. Vehicle systems, instrument panel lights, chimes, and gauges It is important to be familiar with all the controls in the vehicle to avoid searching for a control while driving and possibly being distracted. Certain gauges and lights are more important than others. An easy way to remember the most important gauges and lights is "boil, oil, coil." The first and most important is the temperature or "boil". When this warning light is on or the gauge moves into the red, it means the temperature of the engine coolant is too high and the engine will overheat soon. The proper response to this is to pull over and turn the engine off so it can cool down. Next is the oil gauge or warning light. It signifies that the oil level in the crank case is low. Oil is a lubricant that reduces friction of the metal parts inside the engine. Without it they would create so much friction that eventually the parts will expand and be unable to move freely. This will cause permanent damage to the engine. "Coil" relates to the battery or alternator light or voltage gauge. If trouble is indicated, it means that the battery is not being charged. This is the least urgent of the three warnings. The problem will eventually bring things to a stop, but it doesn't require immediate or emergency attention.
B. safety equipment Lighting- Purpose and use The Vehicle Code specifies:
It is important that your tail, brake, head, and turn lights be in good working order. High beams are generally used in open country when there are few other cars on the road or on dark city streets with no other traffic that would be affected by your high beams. Low beams are used at all other times, including while driving in fog, rain, or heavy snow. Taillights warn you of vehicle ahead of you, and brake lights warn you that the vehicle is slowing down or stopped. Back-up lights, turn signals and emergency flashers similarly serve the purpose of warning other drivers of various maneuvers a vehicle is taking. Headlights. High/low beams You should use your headlights:
You should use your high-beam headlights whenever you are having trouble seeing with your normal headlights, except
You must:
You may flash your headlights to get the attention of another driver so as to avoid an accident.
Taillights Taillights are red taillights, mounted on the rear of a vehicle. Taillights must be visible for 500 feet to the rear. Taillights must be wired so as to be lighted whenever the headlights or auxiliary lights are lighted. The law:
During darkness every motor vehicle
shall be equipped with at least two lighted tail lamps, red in color, which
shall be plainly visible from all distances within 500 feet to the rear. §24600 Brake lights Brake lights must be placed on the rear of the vehicle. Where more than one brake light is required, at least one brake light shall be placed on each side of the rear. Brake lights must be constructed and located on a vehicle so as to give a signal of intention to stop. The law:
Every vehicle, other than a
motorcycle, shall be equipped with two stop lamps, red or yellow in color,
visible from a distance of 300 feet to the rear both during normal sunlight and
at night. §24603 Back-up lights The purpose of backup lights is to:
The law: Every motor vehicle, other than a motorcycle, shall be equipped with one or more backup lamps. Back-up lamps shall be so directed as to project a white light illuminating the highway to the rear of the vehicle for a distance not to exceed 75 feet. §24606
Turn signals You must signal before turning, changing lanes, or otherwise entering traffic from a side road or driveway. You should signal during the last 100 feet before turning unless traffic conditions indicate you should start signaling earlier, such as on a freeway where you should signal for at least 5 seconds before changing lanes. In addition to signaling the intention to make a turn, you must check your mirrors and blind spots to make sure it is safe to complete the maneuver. You should not assume that just because you have signaled a turn or lane change that others can or will leave you the space to complete it. You must signal even when you don't see any cars around. You should use both arm signals and signal lights if it is difficult for others to see your signal lights. If you plan to turn as soon as you leave an intersection, do not start signaling while you are approaching or in the intersection. Wait until you have crossed the intersection so as not to confuse traffic. Make sure that your signal is turned off after you have completed your turn or lane change. The law:
Emergency flashers, hazard lights You can use your hazard warning light flashers:
If emergency flashers are not available, you can tap your brake pedal so as to flash your brake lights to warn drivers behind you of a hazard ahead. Parking lights It is illegal to drive with only your parking lights turned on. Hours of use You should use your lighting as follows:
Visibility requirements You should never drive a vehicle loaded in such a manner that:
You may not carry objects on a passenger vehicle that:
If you are towing a trailer or another vehicle, it must also have its own tail, brake, and turn lights that function simultaneously with those of your vehicle. Signaling and dimming distances You should signal during the last 100 feet before turning. On a freeway, you should signal for at least 5 seconds before changing lanes. You should dim your high beams when an oncoming vehicle gets within 500 feet. Similarly, change to low beams when you get closer than 300 feet of a vehicle ahead of you. Use of brakes The Vehicle Code specifies braking distances that are required for vehicles. These standards differ for different sizes and weights of vehicles, and these distances will be greater for larger, heavier vehicles. You should apply your brakes smoothly to avoid a locked-wheel skid. Anticipate when you will need to stop so you can do so gradually. Smooth, gradual braking will:
A panel indicator showing "ABS" means that a vehicle is equipped with an antilock braking system. If you have an antilock braking system, you should keep constant pressure on the brake pedal while making an emergency stop. If you do not have an antilock braking system, you should use threshold braking (as is outlined in Unit 8). Threshold braking means that you apply and release pressure on your brake pedal in small increments at the skidding threshold. Windshields and mirrors Maintaining good visibility requires that you keep windshields and mirrors clean and free from obstructions. If your windshield is cracked and obstructs your view or that of your passenger, you will not be allowed to take your driving test. You must not carry objects, inside or outside, which obscure your view. You must have mirrors which provide a view for at least 200 feet to the rear of your vehicle. Two mirrors are required on all vehicles. A right side mirror is required and either a rear view or left side mirror. You should properly adjust your mirrors before starting to drive, to avoid being distracted while attempting to adjust them during driving. Over time windshield wipers lose their ability to effectively clean your windshield by cracking, loosing their flexibility, becoming dirty, and getting out of adjustment. Therefore, it is a safe practice is to change them annually. Temperature and humidity conditions may change rapidly causing frost and condensation to quickly form on the windshield. For this reason, it is important to keep the defroster in good operating condition. Do not excessively tint. The Vehicle Code provides specifications for the safe use of sun screening devices and tinting of windows. When cars are manufactured, they are in conformance with these specifications. Any change in tinting or the modification or installation of sun screening devices must be done in accordance with the California Vehicle Code. Horn Vehicles are required to have a functioning horn or similar audible warning device. While the noise level of your horn must not be excessive, it must be audible under normal driving conditions for at least 200 feet from your vehicle. It is appropriate to sound your horn:
It is not appropriate to sound your horn:
Tires The minimum legal tread depth for tires is
To avoid skidding, blowouts, and unsafe handling, the manufacturer's recommendations for your vehicle should be followed in selecting tires. The manufacturer's recommendations for tire pressure should also be followed. Either over- or under-inflating tires:
Failing to keep wheels balanced and the suspension system properly aligned can lead to extremely rapid tire wear and may result in a blow-out. Worn components in the suspension and steering systems of your vehicle can cause you to lose control of your vehicle as well as cause rapid tire wear. The purpose of rotating tires is to prolong the life of the tire. Rotation should be done according to the intervals and procedures recommended by the manufacturer of your vehicle. Peeling out or spinning your tires on fast starts:
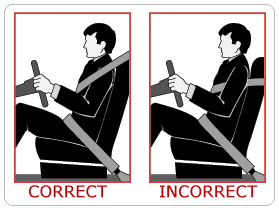
Cornering at high speeds is dangerous, reduces safety margin for emergency maneuvers, and causes excessive tire wear. Safety belts About one person in three will be injured or killed in a traffic accident. Being ejected from a vehicle is one of the most injurious events that can happen to a person in a crash. In fatal crashes, 73% of passenger vehicle occupants who were totally ejected from the vehicle were killed. Unrestrained occupants of a car keep moving during the time the car takes to stop due to inertia. They are still moving forward at their original speed when they slam into the steering wheel, windshield, or other part of the car. This force is equivalent to that of hitting the ground when falling from a three story building. When hit from behind, inertia causes a person's neck to bend backwards, which can result in whiplash. If a vehicle is equipped with seat belts, they must be worn by the driver and all passengers while the vehicle is moving, regardless of whether the vehicle has air bags. If the seat belts have lap and shoulder straps, both must be worn. The purpose of seat belts and shoulder straps is to keep your body from hitting the steering wheel, windshield, or other portions of the interior of your car in a crash. Safety belts are also effective in preventing total ejection from a car in a crash. If you wear only a lap belt when driving, your chances of living through an accident are twice as good as those of someone who isn't. If you wear both a lap and shoulder belt, your chances are three to four time better. While wearing seat belts without shoulder straps can increase chances of spinal and abdominal injury in an accident (especially in children), seat belts alone still reduce overall chances of injury or death. Shoulder harnesses may be available for your vehicle, if it is not already equipped with them. If you are struck from the side in a collision, the impact could push you back and forth across the seat. Seatbelts help to keep you in a better position to control the vehicle. Safety belts can reduce injuries and deaths. Many studies and actual crash tests have proven this fact. Over the past 10 years some 55,600 deaths and 1,300,000 injuries have been prevented by seatbelt use. To be effective, seatbelts must be worn properly. In general, the shoulder belt should fit snuggly against your body, you should never wear the shoulder belt under your arm, you should never wear a seatbelt that is twisted, and you should never be reclined in your seat when moving. Pregnant women should wear lap belts as low a possible under the abdomen and the shoulder strap should be worn between the breasts and the side of the abdomen's bulge.
A lot of misinformation is still given regarding safety-belt usage. The following are examples of some of these safety-belt myths and explanations of why they are incorrect. The belief that safety belts can trap you inside a vehicle is one of these myths. It actually takes less than a second to take off a safety belt. This type of scare tactic often describes a car that caught on fire or sank in deep water. A safety belt may keep you from being knocked out, which will increase your chances of escape in these situations because you are more likely to remain conscious. Another bit of misinformation given regarding safety belts is that, although they are good on long trips, you don't need them if you are just driving around town, to the video store, and so forth. However, half of all traffic deaths occur within 25 miles of the person's home. Don't take chances with your life or the lives of your passengers. You should buckle up every time you drive, even if the trip is local. You also may have heard someone argue that you don't need to wear a seatbelt because some people are thrown clear in a crash and walk away without a scratch. However, your chances of surviving an accident are five times as good if your body remains inside the vehicle during a collision. Safety belts can keep you from being thrown out into the path of another car. Seat belts, adults The use of safety belts ins required by law if the vehicle you are riding or driving in is equipped with them. You and your passengers must wear a safety belt while the vehicle is moving. If not, you or your passenger (if age 16 or older) may be given a traffic citation for not wearing a safety belt. A seat belt is required for each person who is age 6 or older and weighs over 60 pounds. If a child is under 6 years of age, or over 6 years of age but under 60 pounds, the driver, parent, or legal guardian, if present, must put the child in an approved safety seat. S eat belts, childrenMotor vehicle collisions are the leading cause of death or injury to children under five years of age. An adult's arms are not strong enough to hold on to a child during a collision. The forces of a collision are too strong and the weight of an adult can crush a child. Because children are small, they may not benefit from built in safety features inside the vehicle. The back seat is generally the safest place in a vehicle for all children 12 years of age or younger. It has be estimated that when correctly used and installed, child car seats can reduce deaths by about 90% and injuries by 70%. There are special requirements for the use of infant seats and child seats based on the age and weight of the child. Babies up to 20 pounds and about age 1 should ride in a safety seat secured to the back seat facing the rear of the car. Babies should not be placed forward or backward in the front passenger seat if the vehicle is equipped with a passenger-side air bag. Children over 20 pounds and about age 1 or older should ride bucked up in the back seat. Make sure the vehicle's seat belt is put through the correct slots in the safety seat. Incorrectly-fastened safety seat defeat their purpose and can result in injury. Because children can be injured by a seat belt that does not fit correctly, it might be a good idea to use a booster seat designed for use in an automobile for children between 40 and 60 lbs. Don't think that just because you are making a local trip you child, brother, or sister doesn't need to use a car seat. Car accidents are the number one preventable cause of death for children. Take time to buckle them up in safety belts or car seats. It's worth the hassle, and the law requires that you do it. Safety equipment, air bags, adults Air bags, combined with lap/shoulder safety belts, offer the most effective safety protection available today for passenger vehicles. Air bags are designed to provide protection over and above what the seat belt provides. Air bags work best and afford maximum protection in tandem with seat belt use. Seat belts protect you in all crash situations. Air bags, on the other hand, are designed to provide extra protection only in frontal crash situations because people are far more likely to die in a frontal crash than in any other type of crash. Crash sensors trigger air bag deployment when your vehicle experiences a significant frontal or near frontal impact. This causes the solid chemicals within the module to convert to harmless nitrogen gas in a chemical reaction. The expanding gas fills the bag, which opens the cover on the steering wheel hub or the dashboard. When fully expanded, the bag absorbs the forces that the body would normally absorb in the crash. The air bag protects the head and upper body from striking the steering wheel, dashboard or windshield. Most air bag deaths have involved people who weren't using belts, were using them incorrectly, or were positioned improperly. For the maximum air bag protection:
Safety equipment, air bags, children Always seat children in the back seat when possible, even if there is no airbag in front of them. Avoid putting children in the front seat of a car equipped with airbags. Children sitting in the front seat with an air bag could be severely injured by the airbag. Even when kids get older, riding in the back seat is safer. Never install a rear-facing infant safety seat in the front seat of a car equipped with passenger-side air bags, unless the vehicle is equipped with a disabling switch and the switch is in the "off" position. If you must put a child in the front seat, then an airbag on/off switch is essential. If there are too many children to all sit in back, make sure the seat is all the way back and the child is securely buckled and sitting back in the seat. Child safety seats The Law: Effective Jan. 2002, children 60 pounds or less, or 6 years or under, must be restrained in a child passenger restraint system while traveling in a vehicle. Violations of the new law will bring fines of $100 for a first offense and $250 thereafter. The law also authorizes a police officer to stop a vehicle transporting a child who is under the age of 16 and not properly restrained. (§27360)vehicle safety standards. §27360 Child Safety Restraints- Amendment to § 27360 Requires that a child who is required to be secured in a child
safety seat (under 6 years or under 60 pounds) be secured in the rear seat of
the vehicle. A child is allowed to be secured in the front seat of the vehicle
if:
Tips for Using a Child Safety Seat
Built-In Child Seats These permanent seats are designed to restrain children at least 1 year old and 20 pounds. Because they are built into the vehicle, these seats are an effective restraint system for children. They have an advantage over add-on child seats because they do not have a compatibility problem with the vehicle's seat design or safety belt system. Safety belts are required for passengers in pick-up beds Seat belts are required for persons riding in the beds of pick-up trucks. Otherwise, it is illegal to ride in the bed of an open pickup truck. Safety belts maintenance Safety belts must be in good working order to be effective. Safety belts can become ineffective by wear and damage, particularly after an accident, and should be inspected along with other periodic maintenance of the vehicle. It is your responsibility to ensure that the safety belt is in good working order. Check the seat belt and shoulder strap for any worn out spots, or breaks. The clasp must not be broken. Make sure you can still adjust and tighten them. If the seat belt is too loose, it will not stop you from going through the windshield or into the steering wheel, or, being thrown from the car. The Law: Every owner of a motor vehicle, including every owner or operator of a taxicab, or a limousine for hire, operated on a highway shall maintain safety belts in good working order for the use of occupants of the vehicle. §27315
C. maintenance OF THE AUTOMOBILE Vehicle maintenance, tires Tires should be frequently inspected for proper inflation pressure, tread depth, uneven wear, and cracks. They should be replaced when tread depth is low or they are cracked. If uneven wear is present you should check inflation pressure and/or wheel balance and alignment of your vehicle . Have any problems corrected immediately or you may be forced to purchase new tires. Vehicle maintenance, electrical system If the electrolyte in your battery can be refilled, it should be checked and refilled with distilled water as part of regular maintenance on your vehicle in order to keep the battery functioning. Electrolyte fluid is corrosive and can severely injure your eyes. Batteries generate hydrogen gas which can explode when the battery caps are removed. If your alternator belt is slipping or breaks, your battery will discharge, lights and other accessories may not work, and the vehicle will eventually stall. The belt tension should be maintained according to manufacturer specifications for the alternator to perform correctly and to prolong the life of the belt. Cracked belts should be replaced. Exterior lights should be regularly checked for burned out bulbs that you may not be aware of from inside the vehicle. Interior lights are necessary to see displays both at night and during the day, are essential in case of an emergency at night, and must be maintained in proper working order. It is illegal to drive with headlights that are not properly adjusted. It is important to be sure your windshield wiper motor is working and that the linkages to the wipers are functioning. The time to discover there is a problem is not when you need them. Vehicle maintenance, fuel system Leaks in your fuel system can cause fires and expose you to toxic gases. The leaks can occur in the fuel tank, fuel lines, fuel pump, carburetor, fuel injector lines and by not having your gas cap securely attached. If you smell gas you should immediately stop the car, turn off the engine, and determine the problem. Your fuel system should be checked for leaks as part of regular maintenance. Vehicle maintenance, gauges and instruments Speedometer, high beam indicator, turn signal indicator, gear shift position indicator, oil pressure gauge, ammeter, fuel gauge, and engine temperature indicator must all be in good working condition. If a gauge is not working or does not appear to be providing correct information, it should be immediately repaired or replaced. The failure of instruments and panel indicators can lead to incorrect decisions on your part which can cause an accident, break-downs, being stranded, and damage to your engine and other components which could have been avoided. Lighting, heat, and ventilation controls The malfunctioning of the controls can lead to accidents by impairing your visibility and preventing you from being seen by others. Safety aids, emergency tools and equipment It is important to keep the following in your vehicle:
When driving in desolate areas, it is important to be prepared to deal with being stranded due to a break-down by having water, food, and warm clothing available. Periodic lubrication and oil changes Periodic lubrication and oil changes according to manufacturer's recommendations extend the life of your vehicle, allow you to avoid costly repairs, and prevent dangerous break-downs. The weight of oil that you choose for your engine (e.g., 10w-30 or 20w-50) depends on the manufacturer's recommendations, the outside temperature, and the age of your vehicle. Make sure to choose the right weight of oil for your vehicle. Your vehicle uses oil in more than just the engine. Your transmission, differential, and power steering (if equipped) also use fluid that must be periodically checked and changed. Make sure to use the right type of fluid for each. Brakes maintenance Failure or degraded performance of your brakes can lead to accidents. Your brakes should be inspected and maintained according to manufacturer's specifications. You should periodically check the level of your brake fluid and maintain a full level. Periodically change your brake fluid according to the recommendations of your vehicle's manufacturer. Only use the weight of brake fluid they recommend. The level of brake fluid in the master brake cylinder should be checked every time the engine is serviced. Inspection at least twice a year: Brake linings should be checked twice a year and replaced as indicated by inspection. Also, inspection must be done on rubber hoses, lines, fittings, and hydraulic cylinders for leaks. If the brakes squeak, fade, or pull unevenly, they should be checked right away. Engine tune ups and transmission service recommended Periodic tune-ups and transmission service according to manufacturer's specifications extends the life of your vehicle, allows you to avoid costly repairs, and prevents dangerous breakdowns. During a tune up you should have your spark plugs, spark distributor, distributor cap, and air filter changed. The timing of your vehicle should be check and adjusted, and your points should be changed (if your vehicle has them). Shock absorbers/strut operation and security of mounting Shocks absorbers and strut assemblies are important components of your vehicle’s steering and suspension system – they help keep your tires in contact with the road for a smooth, safe ride. Shock absorbers limit the rebounding effect of the springs in your suspension. Struts are components that combine a spring and shock absorber into a single unit Check for fluid leaks
around the shock. Some shocks are filled with oil and a visible fluid leak can
be detected. Excessive bumpy ride, leaning, or swaying in one direction more
than normal on brake application or around turns can also indicate worn or
damaged shocks. Exhaust system Breakdowns and costly repairs can be avoided by keeping your exhaust system in good working order. This includes realizing that changes in noise level, smelling an abnormal amount of fumes, and rattling underneath your vehicle signal problems with your exhaust system. The exhaust system should be inspected for leaks and secure attachment along with other regular maintenance. It is illegal to modify your exhaust system so as to increase the noise level of your vehicle or install a by-pass devise that allows it to increase. Your exhaust system should not have leaks that increase the noise level. Leaks in your exhaust system are dangerous because they expose you to carbon monoxide and other toxic gases. C ooling systemYou must keep your cooling system in good working order. This involves maintaining the level of the coolant and changing it according to manufacturer's recommendations. You should also check for coolant leaks, cracks and deterioration in hoses and belts, and noises and leaks from your water pump. You should replace hoses and belts periodically (recommended, once every three years). Be aware of abrupt changes or trends in your engine temperature as indicated by the temperature gauge. These signal developing problems.
Steering and wheel alignment inspection/service To avoid breakdowns, accidents, and costly repairs, you should be aware of the condition of your steering system. There should be no play in your steering wheel if you have power steering, and no more than 2 inches of play in your steering wheel if you do not have power steering. If this is not the case, you should have your vehicle checked-out by a qualified technician. Vibrations, unusual noises from your wheels, and your vehicle pulling or swerving when you stop or turn all indicate possible problems in your suspension system, steering system, brake system, and/or wheels and tires. These problems are largely avoided by inspection and repair at regular intervals. Wheel alignment. In its most basic form, a wheel alignment consists of adjusting the angles of the wheels so that they are perpendicular to the ground and parallel to each other. The purpose of these adjustments is maximum tire life and a vehicle that tracks straight and true when driving along a straight and level road. Proper wheel alignment reduces tire wear, improves fuel economy and handling, while increasing driving enjoyment and safety. Have your car's alignment checked once a year. Normal wear and road conditions can take their toll on your car's steering and suspension system, possibly throwing the alignment settings out of specifications. Some common symptoms of your car needing an alignment include uneven tire tread wear, pulling to one side, wandering, and an off-center steering wheel. Smog control devices The law requires (in most cases) that you have an emission test every two years at the time of registration or at time of sale. It is a good idea to have your smog control components checked at the time of a tune-up. Ensure that smog control devices are intact and connected properly.
D. Economic AND SAFE USE OF THE AUTOMOBILE Economical operation There are several things you can do to maximize the economic operation of your motor vehicle. First, you should avoid making fast starts and stops, and cornering too fast. They are not only unsafe, but increase the cost of operating and maintaining your vehicle by wasting fuel and wearing out tires and brakes. The second thing you can do to save money is to drive slower. Faster driving requires more fuel to get you the same distance. Obey speed limits and you will save fuel and reduce the risk to others. Another thing you can do is to anticipate when you will need to stop. Quick braking excessively wears your brakes and tires. Look ahead while you are driving so you can anticipate when you will need to stop and do so smoothly and gently. Periodic or preventative maintenance of your vehicle will also lower your long-term operation costs. Periodic tune ups reduce fuel consumption by making your vehicle run more efficiently. The money you spend on periodic maintenance can also save you large expenses due to major engine failure and breakdown. Calculating overall operational costs There are costs:
The cost of owning and operating a vehicle is the sum of those costs directly related to the number of miles driven (gasoline, replacing tires and other components that wear out with use, and oil changes), and costs that are largely the same regardless of how little you actually drive your car (insurance, registration, depreciation, and maintenance that must be performed regardless of miles driven). Depreciation is a significant cost in owning a vehicle. Depreciation is the amount you have paid for the privilege of owning and driving the vehicle in addition to what you have paid for gas, maintenance, insurance, and so on. As your car accumulates more miles or gets older (regardless of how many miles it has been driven), it is worth less when you sell it. Depreciation is particularly high during the period immediately after buying a new car, and the yearly depreciation cost decreases as the car gets older. If you drive your car very little, gas mileage, and maintenance may not be a significant consideration, but depreciation, insurance, and registration will be. If you drive your car a lot, gas mileage and day-to-day repairs will be significant cost considerations. While it is difficult to estimate the costs of owning and operating a vehicle precisely, you should consider all of these types of costs when making a decision about what type of vehicle to purchase.
|
 Content
Of Online Course
Content
Of Online Course